We believe that the Amazon is not for sale, nor is it for expanding a primitive source for fuel. Here is a link where you can join a petition by our good friends at AmazonWatch. – Valhalla mgnt
http://amazonwatch.org/take-action/stand-with-the-sapara-people-to-reject-todays-sham-contract
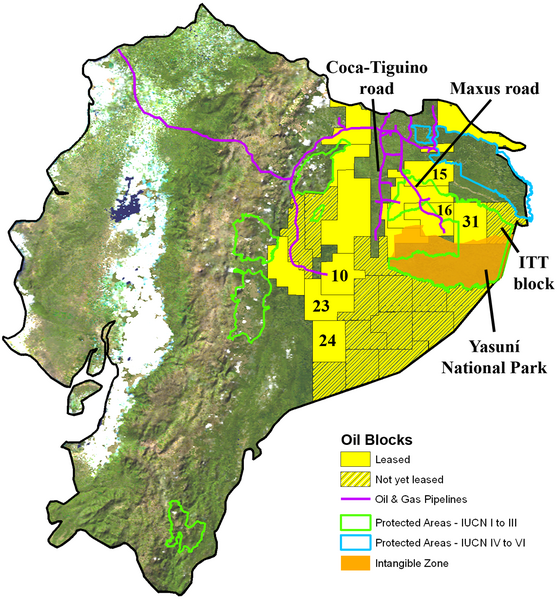
Ecuador is planning to auction off three million of the country’s 8.1 million hectares of pristine Amazonian rainforest to Chinese oil companies, Jonathan Kaiman of The Guardian reports.
The report comes as oil pollution forced neighbouring Peru to declare an environmental state of emergency in its northern Amazon rainforest.
Ecuador owed China more than $7 billion – more than a tenth of its GDP – as of last summer.
In 2009 China began loaning Ecuador billions of dollars in exchange for oil shipments. It also helped fund two of the country’s biggest hydroelectric infrastructure projects, and China National Petroleum Corp may soon have a 30 per cent stake in a $10 billion oil refinery in Ecuador.
“My understanding is that this is more of a debt issue – it’s because the Ecuadoreans are so dependent on the Chinese to finance their development that they’re willing to compromise in other areas such as social and environmental regulations,” Adam Zuckerman, environmental and human rights campaigner at California-based NGO Amazon Watch, told the Guardian.
The seven indigenous groups who live on the land are not happy, especially because last year a court ruled that governments must obtain “free, prior, and informed consent” from native groups before approving oil activities on their indigenous land.
“They have not consulted us, and we’re here to tell the big investors that they don’t have our permission to exploit our land,” Narcisa Mashienta, a leader of Ecuador’s Shuar people, said in a report.
Dan Collyns of The Guardian reports that “indigenous people living in the Pastaza river basin near Peru’s border with Ecuador have complained for decades about … pollution,” which has been caused by high levels of petroleum-related compounds in the area. The Argentinian company Pluspetrol has operated oil fields there since 2001.