Fact Coexist
Fact Coexist
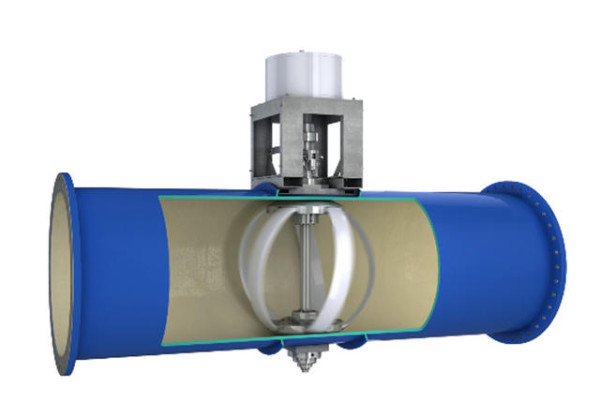
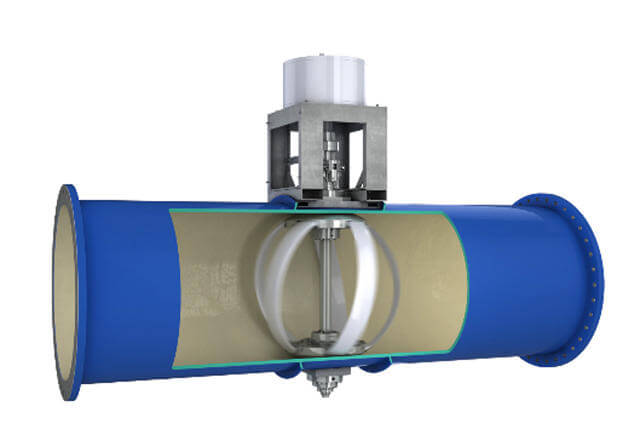
If you live in Portland, your lights may now be partly powered by your drinking water. An ingenious new system captures energy as water flows through the city’s pipes, creating hydropower without the negative environmental effects of something like a dam.
Small turbines in the pipes spin in the flowing water, and send that energy into a generator.
“It’s pretty rare to find a new source of energy where there’s no environmental impact,” says Gregg Semler, CEO of Lucid Energy, the Portland-based startup that designed the new system. “But this is inside a pipe, so no fish or endangered species are impacted. That’s what’s exciting.”
For water utilities, which use massive amounts of electricity, the system can make it cheaper to provide clean drinking water. Utilities can either use the power themselves or sell it to a city as a new source of revenue.
“We have a project in Riverside, California, where they’re using it to power streetlights at night,” Semler says. “During the day, when electricity prices are high, they can use it to offset some of their operating costs.”
In Portland, one of the city’s main pipelines now uses Lucid’s pipes to make power that’s sent into the grid. Though the system can’t generate enough energy for an entire city, the pipes can power individual buildings like a school or library, or help offset a city’s total energy bill. Unlike wind or solar power, the system can generate electricity at any time of day, regardless of weather, since the pipes always have water flowing through them.
The pipes can’t generate power in every location; they only work in places where water is naturally flowing downward with gravity (if water is being pumped, the system would waste energy). But they have another feature that can be used anywhere: The pipes have sensors that can monitor water, something that utilities couldn’t do in the past.
“We made electrical infrastructure really smart over the last 20 to 25 years, but the same hasn’t happened in water,” Semler says. He points to the example of a pipe that burst near UCLA last year, wasting a staggering 20 million gallons of water in the middle of California’s crippling drought.
“They didn’t really know that the pipe burst until somebody from UCLA called,” Semler explains. “Our pipe can get indicators like pressure, a leading indicator for whether a pipe is leaking or not. So before it bursts and before we waste all the water, there are onboard information systems that water agencies can get to more precisely manage their infrastructure.”
Sensors in the pipe can also monitor water quality, making sure it’s safe to drink.
The company hopes to work with cities to install new systems as old pipes wear out. They’re also hoping to expand to the developing world. “It’s a great source of remote power,” says Semler. “So in places outside the city that don’t have an electrical grid, you’re able to use the system to generate energy.”
The biggest potential for the new system may be in places like California, where 20% of total energy use goes into the water supply-and even more electricity will be used as cities start to install desalination plants. With the pipes, utilities can generate some of their own much-needed power.
“There’s a lot of energy in going into making sure we have safe clean drinking water,” Semler says. “Our focus is really on helping water become more sustainable.”